Medical devices play a vital role in helping physicians perform various medical and surgical procedures that improve the health of their patients. The World Health Organization defines a medical device as “an article, instrument, apparatus or machine that is used in the prevention, diagnosis or treatment of illness or disease, or for detecting, measuring, restoring, correcting or modifying the structure or function of the body for some health purpose.”
Medical devices manufacturing represents one of the largest segments of the health care industry, fueled by innovation and the almost constant emergence of new technologies. The United States is the most prolific global player in the medical devices industry, with annual sales of approximately $136 billion, which represents about 45 percent of the global market as of 2014. The top U.S. medical device manufacturers by revenue are Johnson & Johnson, General Electric, Medtronic, Baxter International and Cardinal Health.
The medical devices industry consists of several subsectors, including:
- Medical and surgical instruments
- Surgical appliances and supplies
- Irritation apparatuses
- In-vitro diagnostics
- Electro-medical equipment
The variety of devices within these subsectors ranges from heart pacemakers to CT scanners. Recent advancements in technology have led to the development of innovative products such as cardiac stents, biomarkers, implantable electronic devices and neuro-stimulators. The growing population of older Americans should continue to foster the consistent growth of the medical devices industry for years to come.
The Need for Electroplating of Medical Devices
While there are numerous types of medical devices on the market these days, what many have in common is the need for an application of a protective metal coating during the manufacturing process. One of the more common metal coating procedures is electroplating, which entails the application of dissolved metal ions onto the surface of the workpiece via electrodeposition. An electric current is introduced into a solution consisting of the metal ions and other chemical additives, which causes them to bond to the object.
Reasons for electroplating medical devices include:
- Facilitating electrical conductivity — Certain medical devices require the transmission of an electric current to function properly. Many types of metals, especially gold, silver and copper, are excellent conductors of electricity and are able to carry current efficiently.
- Promoting thermal conductivity — Thermal conductivity refers to the rate at which heat passes through a material. Several metals exhibit high levels of thermal conductivity, which enables the electroplated device to carry heat away from the body. This minimizes the risk of burns and the formation of adhesions.
- Increasing wear resistance — Heavily used medical devices and surgical instruments can experience wear and tear that can result in their premature demise. A metal coating can increase the device’s wear resistance and lengthen its lifespan.
- Improving corrosion resistance — Implants, pacemakers and other medical devices that are implanted in the human body are exposed to moisture that can eventually cause corrosion. Electroplating can provide a protective barrier that will prevent rust formation.
- Creating compatibility between different metals — Some medical devices are manufactured with several types of metals that must be welded together, which can prove challenging. Coating the pieces with a metal such as gold or nickel can make them compatible to welding, which improves the quality of the finished product.
- Providing biocompatibility — Some medical devices, particularly implants or other devices that are placed inside the body, must be biocompatible, meaning they won’t pose harm to human tissue. Certain medical coatings will render the underlying material biocompatible, making it safe for use in various medical and surgical procedures.
- Promoting cleanliness and sanitation — There are few industries where cleanliness is more important than health care. Various metals feature antimicrobial characteristics that can ward off bacteria and resist infections. These coatings will not wear off, which ensures the longevity of the protective properties.
- Creating radiopaque features — The term “radiopaque” means a material is not transparent to X-rays or other forms of radiation. Coating a medical device with gold or another high-density metal will establish a radiopaque area that can be detected via radiography, meaning the gold can block the radiation emitted by the X-rays.
- Coating braided shafts — Catheters and other minimally invasive medical devices that are used in applications requiring high torque, steerability and burst pressure resistance often feature braided shafts. An electroplated coating can provide an adhesive bond that locks the braids together and improves the device’s accuracy.
Overview of Gold Plating for Medical Instruments
Various metals are good for electroplating medical devices, including silver, tin, nickel, copper — and gold. While most of us think of gold for its aesthetic quality, it also exhibits several properties that make it well-suited for coating medical instruments. Gold plating for medical implants has become a common practice, and you’ll also find gold coatings on everything from stents and electronic pacemakers to electrical contacts and even the laser equipment used by military medical personnel to treat battlefield injuries.
Benefits of Medical Device Gold Plating
While gold is not the least expensive metal, especially compared to much less pricey non-precious metals such as nickel, tin and copper, it is the preferred plating option for many medical device manufacturing applications. Manufacturers understand gold’s exceptional quality can make it the most cost-effective choice in the long run and enable it to provide the best return on investment for the manufacturer, as well as the medical device consumer.
Specific attributes of medical-grade gold plating include:
- Malleability — Gold is a softer and more malleable metal, which provides the flexibility manufacturers need when producing the complex, high-precision products that epitomize many medical devices. It is relatively easy to “shape” a gold coating via the electroplating process to conform to the configuration of the device, resulting in higher quality and improved performance of the product.
- Excellent corrosion resistance — Gold will not oxidize when exposed to open air, which means it is highly resistant to the formation of rust. Acids and other corrosive materials also will not affect a gold coating. Surgeons can insert gold-plated medical devices inside the human body with no concerns about corrosion negating the device’s long-term safety and performance.
- Biocompatible — Gold is also one of the most biocompatible metals. It will not create adverse or toxic reactions when coming in contact with the skin, tissue or internal organs. This also reduces the risk of post-operative infections after the insertion of an implant, pacemaker or stent.
- Density — Gold features a density of 19.32 g/cm3 — grams per cubic centimeter — meaning gold weighs about 19 times as much as an equal volume of water at a temperature of 68° F. This high density makes gold an extremely radiopaque material that is opaque to X-rays.
- Visibility — The inherent brightness of gold makes it extremely visible when inserted inside the body. Surgeons can implant a gold-plated device with a high level of accuracy. Health care practitioners can quickly and easily locate an inserted medical device with a fluoroscopy machine, which assists them in assessing its performance and safety.
- Electrical conductivity — Gold exhibits exceptional long-term electrical conductivity, making it well-suited for devices containing electrical or electronic parts and components such as contacts and connector pins.
- Weldability/solderability — The gold electroplating process will provide a secure connection when soldering or welding dissimilar metals together, such as when enjoining nickel-titanium alloy with stainless steel while manufacturing a medical implant.
Gold Plating Applications for Medical Devices
There are numerous applications for gold-plated medical devices, and emerging technologies are leading to new innovations on a frequent basis. Examples include:
- Stents — A stent is a small metal mesh tube commonly used to facilitate blood flow in blocked or narrow arteries. Gold plating is used for various types of stents that require radiopacity, such as laser-slotted hypotubes, as well as stents that require laser cutting.
- Pacemakers — A pacemaker is a medical device that regulates the beating of the heart. Gold enhances conductivity for the pacemaker’s electrical components and also provides protection against corrosion.
- Implants — The use of implanted devices such as hip and knee joints is now commonplace in the health care profession for replacing damaged body parts or providing structural support. The gold plating of implants will improve the biocompatibility of the devices, making them safer for the patient.
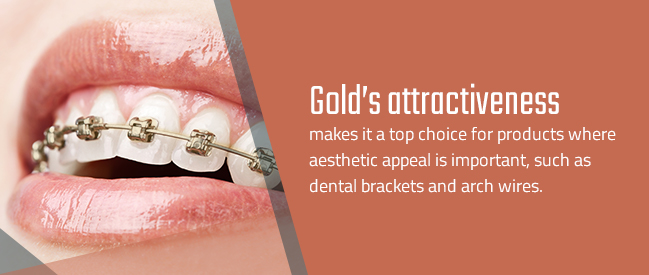
- Dental devices — Gold’s attractiveness makes it a top choice for products where aesthetic appeal is important, such as dental brackets and arch wires. Gold’s high quality also ensures the longevity and safety of dental products that are inserted in the patient’s mouth.
- Casings for batteries — Many electrical medical devices operate via battery power. Gold plating can provide a protective coating for the batteries’ casing by offering reliable corrosion resistance. Plating gold onto battery casings can also be an extremely cost-effective process, as it eliminates the need for applying additional base coatings.
- Housings — Many medical devices feature metallic housings that protect their complex, delicate inner components. Gold plating provides an additional layer of protection of the housings that will prevent corrosion and increase wear resistance.
- Scopes — Various medical and surgical procedures are now performed via minimally invasive techniques that create less trauma for the patient and can shorten the recovery period. Many of these procedures rely on tools such as endoscopes and arthroscopes, which consist of gold-plated components to protect against corrosion.
- Metallization of plastics — Certain medical devices are made of polymers or include plastic components that do not conduct electricity. Other devices may contain electrical circuit boards that require a metal coating to promote conductivity. An electroplated gold coating will adhere well to the surface of the substrate and supply the necessary conductivity. Depending on the process, it may be possible to apply the gold coating without an underlying metal base coat.
Medical Devices Gold Plating: Two Examples
Here are two examples of how a metal finishing company can apply gold plating for medical devices to resolve challenging manufacturing issues.
- Scenario 1: Coating a battery casing for an insulin pump — An insulin pump is a medical device that delivers precise doses of insulin during diabetic treatment procedures. The casing that houses the pump’s batteries must include a gold coating to protect against corrosion. An experienced gold plating services provider can develop a customized process that combines a gold coating with palladium and nickel to meet the project’s plating needs, while meeting the quantity requirements in a cost-effective manner.
- Scenario 2: Fusing a nickel-titanium alloy to other materials — Many medical devices are made with a nickel-titanium (Ni-Ti) alloy due to its excellent corrosion resistance, elasticity and biocompatibility. However, it is difficult to weld Ni-Ti to other materials such as stainless steel. Gold plating the ends of the Ni-Ti and stainless steel before welding creates a fusible region that strengthens the weld.
The Medical Device Gold Plating Process
It is possible to apply gold plating to medical devices by either the barrel or rack methods. Barrel plating entails placing the parts inside a drum-like device. The next step is to place the drum in a plating solution consisting of dissolved gold ions and chemical additives and rotate it slowly to apply the coating. Barrel plating works best for high-volume projects featuring larger parts and components.
Another option for coating medical devices with gold is rack plating. The rack plating method involves affixing the workpiece to a rack and submersing it into the plating solution. Rack plating is the preferred method for plating smaller, more delicate medical device parts that could sustain damage from the more volatile barrel plating process.
When performing gold plating for medical devices that involves welding or soldering, thorough rinsing after plating is essential for ensuring proper adhesion of the gold coating. After rinsing, the parts should be dried in a stainless steel oven to ensure the evaporation of residual water. Nitrogen bag packaging of the plated parts will preserve the purity of the gold coating.
Sharretts Plating Company Offers Expert Gold Plating Services for Medical Devices
Experience is an important consideration when selecting a metal finishing company for the application of gold plating for medical devices. With our more than 90 years of electroplating experience, you can trust SPC to develop a customized gold plating process that provides the ideal finishing solution for your medical devices.
We’re proficient at both barrel and rack plating as it applies to medical devices — we can accommodate smaller and larger workpieces for small and large-volume projects. Our state-of-the-art York, Pa., facility features the most advanced electroplating equipment to ensure the best results while meeting your tight project deadlines.
At SPC, we make quality the top priority for everything we do. We’re an ISO-certified metal finishing operation that implements advanced quality management systems and stringent quality control procedures. Our team consists of experienced, well-trained professionals in every area of our company, from our scientists and engineers to our production and shop floor personnel. What’s more, we take a consultative approach to the metal finishing process that enables us to adapt our methodologies to the unique needs of our customers, regardless of project size or scope.
Contact Us to Learn More About Our Gold Plating Services for Medical Devices
Learn more about the many ways in which gold plating can benefit your medical device manufacturing processes. Contact the gold plating experts at SPC to obtain a no-obligation project quote or schedule an onsite consultation today.